D.C. motors are constructed to operate continuously within a range of speeds near their no-load speed. This range of speeds is generally too high for most applications. In order to reduce this speed, a full range of geared motors is available, each with a series of gear ratios to suit most speed requirements.The complete range is suitable for a wide variety of applications.
●Gearbox characteristics:
Our gearboxes have been designed for optimum performance and for maximum life under normal operating conditions.Their main characteristic is the capacity to withstand maximum design torque with continuous duty.The range of gearboxes shown in this catalogue can operate with maximum torque of 0.5 to 6 N.m for long time periods. All values previously stated are for standard products in normal operating conditions, as specified.In certain cases, these values may be increased if a shorter life is required.Please consult our Sales Office for further information.Every gearbox has a torque limit, which is the breaking torque If this torque is applied to the gearbox, it will cause severe damage.
●Gearbox construction
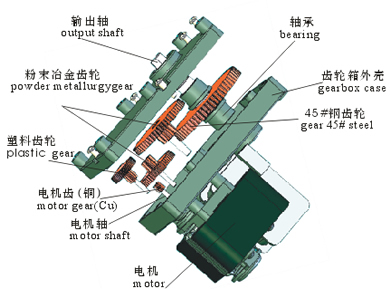
The module,depth and material of Gears are calculated according to the stress of gear at each step. By life test of motor to produce the motor with low noise and enough life time. Gearbox can be assembled with DC motors, DC brushless motors and shade pole motors.
●Selection of a geared motor:
A geared motor is selected according to the required usable power output.
useableP(W)= 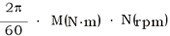
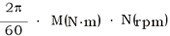
useableP(W)=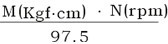
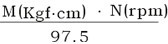
useableP(W)= 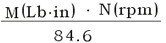
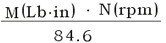
useableP(W)=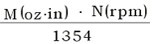
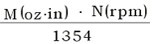
●Selecting the reduction gear ratio:
Two selection criteria may be applied.
* The first criterion concerns the required speed output of the reduction gear only. It is adequate for most applications and is easy to apply. Given that :
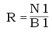 N1= required speed of geared motor B1=basic nominal speed of motor
N1= required speed of geared motor B1=basic nominal speed of motor
The second criterion concerns the required usable power output of the motor.
●The rotational speed of the motor is given by :
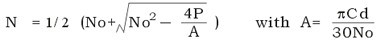
N = speed of motor(rpm) No = no loadspeed of motor(rpm)
P = required output power(W) Cd = start-up torque of motor(Nm)
this gives the equation: 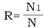
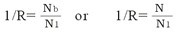
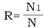
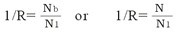
In order to avoid using numbers less than 1 where the reduction ratio is concerned, the value 1/R is employed. Due to the fact that it is always a reduction gear and not a "ultiplier" gear, there should be no ambiguity concerning the number used.

